Showing posts with label Visual Basic GTK#. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Visual Basic GTK#. Show all posts
Tuesday, April 16, 2013
The Nibbles Clone using Visual Basic GTK#
Nibbles
In this part of the Visual Basic GTK# programming tutorial, we will create a Nibbles game clone.Nibbles is an older classic video game. It was first created in late 70s. Later it was brought to PCs. In this game the player controls a snake. The objective is to eat as many apples as possible. Each time the snake eats an apple, its body grows. The snake must avoid the walls and its own body.
Development
The size of each of the joints of a snake is 10px. The snake is controlled with the cursor keys. Initially, the snake has three joints. The game starts immediately. When the game is finished, we display "Game Over" message in the center of the window.board.vb
Imports GtkFirst we will define some globals used in our game.
Imports Cairo
NameSpace BoardSpace
Public Class Board
Inherits DrawingArea
Const WIDTH As Integer = 300
Const HEIGHT As Integer = 300
Const DOT_SIZE As Integer = 10
Const ALL_DOTS As Integer = 900
Const RAND_POS As Integer = 30
Const DELAY As Integer = 140
Dim x(ALL_DOTS) As Integer
Dim y(ALL_DOTS) As Integer
Dim dots As Integer
Dim apple_x As Integer
Dim apple_y As Integer
Dim left As Boolean = False
Dim right As Boolean = True
Dim up As Boolean = False
Dim down As Boolean = False
Dim inGame As Boolean = True
Dim dot As ImageSurface
Dim apple As ImageSurface
Dim head As ImageSurface
Public Sub New
MyBase.New
ModifyBg(StateType.Normal, New Gdk.Color(0, 0, 0))
Me.InitGame
End Sub
Private Sub InitGame
dots = 3
For z As Integer = 0 To dots-1
x(z) = 50 - z*10
y(z) = 50
Next
Try
dot = New ImageSurface("dot.png")
head = New ImageSurface("head.png")
apple = New ImageSurface("apple.png")
Catch
Console.WriteLine("Images not found")
Environment.Exit(1)
End Try
Me.LocateApple
Dim timer As New GLib.TimeoutHandler(AddressOf Me.OnTimer)
GLib.Timeout.Add(100, timer)
AddHandler Me.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExpose
End Sub
Protected Sub OnExpose(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As ExposeEventArgs)
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)
If inGame
Me.DrawObjects(cc)
Else
Me.GameOver(cc)
End If
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)
disposeTarget.Dispose
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose
End Sub
Private Sub DrawObjects(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
cc.SetSourceSurface(apple, apple_x, apple_y)
cc.Paint
For z As Integer = 0 to dots - 1
If z = 0
cc.SetSourceSurface(head, x(z), y(z))
cc.Paint
Else
cc.SetSourceSurface(dot, x(z), y(z))
cc.Paint
End If
Next
End Sub
Private Sub GameOver(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
Dim message As String = "Game Over"
Dim x As Integer = Allocation.Width / 2
Dim y As Integer = Allocation.Height / 2
cc.SetSourceRGB(1, 1, 1)
cc.SetFontSize(18)
Dim extents As TextExtents = cc.TextExtents(message)
cc.MoveTo(x - extents.Width/2, y)
cc.ShowText(message)
inGame = False
End Sub
Private Sub CheckApple
If x(0) = apple_x And y(0) = apple_y
dots += 1
Me.LocateApple
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Move
For z As Integer = dots To 1 Step -1
x(z) = x(z - 1)
y(z) = y(z - 1)
Next
If left
x(0) -= DOT_SIZE
End If
If right
x(0) += DOT_SIZE
End If
If up
y(0) -= DOT_SIZE
End If
If down
y(0) += DOT_SIZE
End If
End Sub
Private Sub CheckCollision
For z As Integer = dots To 1 Step -1
If z > 4 And x(0) = x(z) And y(0) = y(z)
inGame = False
End If
Next
If y(0) > HEIGHT
inGame = False
End If
If y(0) < 0
inGame = False
End If
If x(0) > WIDTH
inGame = False
End If
If x(0) < 0
inGame = False
End If
End Sub
Private Sub LocateApple
Dim rand As New Random
Dim r As Integer = rand.Next(RAND_POS)
apple_x = r * DOT_SIZE
r = rand.Next(RAND_POS)
apple_y = r * DOT_SIZE
End Sub
Private Function OnTimer As Boolean
If inGame
Me.CheckApple
Me.CheckCollision
Me.Move
Me.QueueDraw
Return True
Else
Return False
End If
End Function
Public Sub OnKeyDown(ByVal e As Gdk.EventKey)
Dim key As Integer = e.KeyValue
If key = Gdk.Key.Left AndAlso Not right
left = True
up = False
down = False
End If
If key = Gdk.Key.Right AndAlso Not left
right = True
up = False
down = False
End If
If key = Gdk.Key.Up AndAlso Not down
up = True
right = False
left = False
End If
If key = Gdk.Key.Down AndAlso Not up
down = True
right = False
left = False
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The WIDTH and HEIGHT constants determine the size of the Board. The DOT_SIZE is the size of the apple and the dot of the snake. The ALL_DOTS constant defines the maximum number of possible dots on the Board. The RAND_POS constant is used to calculate a random position of an apple. The DELAY constant determines the speed of the game.
Dim x(ALL_DOTS) As IntegerThese two arrays store x, y coordinates of all possible joints of a snake.
Dim y(ALL_DOTS) As Integer
The InitGame method initializes variables, loads images and starts a timeout function.
If inGameInside the OnExpose method, we check the inGamevariable. If it is true, we draw our objects. The apple and the snake joints. Otherwise we display "Game over" text.
Me.DrawObjects(cc)
Else
Me.GameOver(cc)
End If
Private Sub DrawObjects(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)The DrawObjects method draws the apple and the joints of the snake. The first joint of a snake is its head, which is represented by a red circle.
cc.SetSourceSurface(apple, apple_x, apple_y)
cc.Paint
For z As Integer = 0 to dots - 1
If z = 0
cc.SetSourceSurface(head, x(z), y(z))
cc.Paint
Else
cc.SetSourceSurface(dot, x(z), y(z))
cc.Paint
End If
Next
End Sub
Private Sub CheckAppleThe CheckApple method checks, if the snake has hit the apple object. If so, we add another snake joint and call the LocateApple method, which randomly places a new apple object.
If x(0) = apple_x And y(0) = apple_y
dots += 1
Me.LocateApple
End If
End Sub
In the Move method we have the key algorithm of the game. To understand it, look at how the snake is moving. You control the head of the snake. You can change its direction with the cursor keys. The rest of the joints move one position up the chain. The second joint moves where the first was, the third joint where the second was etc.
For z As Integer = dots To 1 Step -1This code moves the joints up the chain.
x(z) = x(z - 1)
y(z) = y(z - 1)
Next
If leftMove the head to the left.
x(0) -= DOT_SIZE
End If
In the CheckCollision method, we determine if the snake has hit itself or one of the walls.
For z As Integer = dots To 1 Step -1Finish the game, if the snake hits one of its joints with the head.
If z > 4 And x(0) = x(z) And y(0) = y(z)
inGame = False
End If
Next
If y(0) > HEIGHTFinish the game, if the snake hits the bottom of the Board.
inGame = False
End If
The LocateApple method locates an apple randomly on the board.
Dim rand As New RandomWe get a random number from 0 to RAND_POS - 1.
Dim r As Integer = rand.Next(RAND_POS)
apple_x = r * DOT_SIZEThese line set the x, y coordinates of the apple object.
...
apple_y = r * DOT_SIZE
If inGameEvery 140 ms, the OnTimer method is called. If we are in the game, we call three methods, that build the logic of the game. Otherwise we return False, which stops the timer event.
Me.CheckApple
Me.CheckCollision
Me.Move
Me.QueueDraw
Return True
Else
Return False
End If
In the OnKeyDown method of the Board class, we determine the keys that were pressed.
If key = Gdk.Key.Left AndAlso Not rightIf we hit the left cursor key, we set left variable to true. This variable is used in the Movemethod to change coordinates of the snake object. Notice also, that when the snake is heading to the right, we cannot turn immediately to the left.
left = True
up = False
down = False
End If
nibbles.vb
' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn this class, we set up the Nibbles game.
'
' In this program, we create
' a Nibbles game clone
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Dim WIDTH As Integer = 250
Dim HEIGHT As Integer = 150
Dim board As BoardSpace.Board
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Nibbles")
board = New BoardSpace.Board
Me.Add(board)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.Resize(310, 310)
Me.Move(300, 300)
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Protected Overrides Function OnKeyPressEvent(ByVal e As Gdk.EventKey) As Boolean
board.OnKeyDown(e)
Return True
End Function
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Protected Overrides Function OnKeyPressEvent(ByVal e As Gdk.EventKey) As BooleanIn this class, we catch the key press events. And delegate the processing to the OnKeyDown method of the board class.
board.OnKeyDown(e)
Return True
End Function
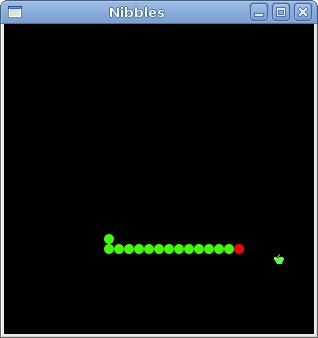
Figure: Nibbles
The following command compiles the game. vbnc -r:/usr/lib/mono/gtk-sharp-2.0/gtk-sharp.dll
-r:/usr/lib/mono/gtk-sharp-2.0/gdk-sharp.dll -r:/usr/lib/mono/2.0/Mono.Cairo.dll
-r:/usr/lib/mono/gtk-sharp-2.0/glib-sharp.dll nibbles.vb board.vb
This was the Nibbles computer game programmed with the GTK# library and the Visual Basic programming language.
Custom widget in Visual Basic GTK#
Custom widget
Have you ever looked at an application and wondered, how a particular gui item was created? Probably every wannabe programmer has. Then you were looking at a list of widgets provided by your favourite gui library. But you couldn't find it. Toolkits usually provide only the most common widgets like buttons, text widgets, sliders etc. No toolkit can provide all possible widgets.There are actually two kinds of toolkits. Spartan toolkits and heavy weight toolkits. The FLTK toolkit is a kind of a spartan toolkit. It provides only the very basic widgets and assumes, that the programemer will create the more complicated ones himself. wxWidgets is a heavy weight one. It has lots of widgets. Yet it does not provide the more specialized widgets. For example a speed meter widget, a widget that measures the capacity of a CD to be burned (found e.g. in nero). Toolkits also don't have usually charts.
Programmers must create such widgets by themselves. They do it by using the drawing tools provided by the toolkit. There are two possibilities. A programmer can modify or enhance an existing widget. Or he can create a custom widget from scratch.
Burning widget
This is an example of a widget, that we create from scratch. This widget can be found in various media burning applications, like Nero Burning ROM.custom.vb
Imports GtkWe put a DrawingArea on the bottom of the window and draw the entire widget manually. All the important code resides in the DrawCustomWidget which is called from the OnExpose method of the Burning class. This widget shows graphically the total capacity of a medium and the free space available to us. The widget is controlled by a scale widget. The minimum value of our custom widget is 0, the maximum is 750. If we reach value 700, we began drawing in red colour. This normally indicates overburning.
NameSpace BurningWidget
Public Class Burning
Inherits DrawingArea
Const PANEL_HEIGHT As Integer = 30
Const DIVISIONS As Integer = 10
Const FULL_CAPACITY As Double = 700
Const MAX_CAPACITY As Double = 750
Dim redColor As New Gdk.Color(1, 0.7, 0.7)
Dim yellowColor As New Gdk.Color(1, 1, 0.7)
Dim parent As Widget
Dim num() As String = { _
"75", "150", "225", "300", _
"375", "450", "525", "600", _
"675" _
}
Public Sub New(ByVal parent As Widget)
Me.SetSizeRequest(1, PANEL_HEIGHT)
Me.parent = parent
AddHandler Me.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExpose
End Sub
Private Sub OnExpose(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As ExposeEventArgs)
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)
Me.DrawCustomWidget(cc)
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)
disposeTarget.Dispose
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose
End Sub
Private Sub DrawCustomWidget(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
cc.LineWidth = 0.8
cc.SelectFontFace("Courier 10 Pitch", _
Cairo.FontSlant.Normal, Cairo.FontWeight.Normal)
cc.SetFontSize(11)
Dim burn As Custom.GtkVBApp = CType(parent, Custom.GtkVBApp)
Dim slid_width As Double = burn.GetCurrentWidth
Dim width As Double = Allocation.Width
Dim move As Double = width / DIVISIONS
Dim till As Double = (width / MAX_CAPACITY) * slid_width
Dim full As Double = (width / MAX_CAPACITY) * FULL_CAPACITY
If slid_width >= FULL_CAPACITY
cc.SetSourceRGB(1.0, 1.0, 0.72)
cc.Rectangle(0, 0, full, PANEL_HEIGHT)
cc.Clip
cc.Paint
cc.ResetClip
cc.SetSourceRGB(1.0, 0.68, 0.68)
cc.Rectangle(full, 0, till-full, PANEL_HEIGHT)
cc.Clip
cc.Paint
cc.ResetClip
Else
cc.SetSourceRGB(1.0, 1.0, 0.72)
cc.Rectangle(0, 0, till, PANEL_HEIGHT)
cc.Clip
cc.Paint
cc.ResetClip
End If
cc.SetSourceRGB(0.35, 0.31, 0.24)
For i As Integer = 1 To num.Length
cc.MoveTo(i*move, 0)
cc.LineTo(i*move, 5)
cc.Stroke
Dim extents As Cairo.TextExtents = cc.TextExtents(num(i-1))
cc.MoveTo(i*move-extents.Width/2, 15)
cc.TextPath(num(i-1))
cc.Stroke
Next
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Dim num() As String = { _
"75", "150", "225", "300", _
"375", "450", "525", "600", _
"675" _
}
These numbers are shown on the burning widget. They show the capacity of the medium. Dim burn As Custom.GtkVBApp = CType(parent, Custom.GtkVBApp)These two lines get the current number from the scale widget. We get the parent widget and from the parent widget, we get the current value.
Dim slid_width As Double = burn.GetCurrentWidth
Dim till As Double = (width / MAX_CAPACITY) * slid_widthWe use the width variable to do the transformations. Between the values of the scale and the custom widget's measures. Note that we use floating point values. We get greater precision in drawing. The till parameter determines the total size to be drawn. This value comes from the slider widget. It is a proportion of the whole area. The full parameter determines the point, where we begin to draw in red color.
Dim full As Double = (width / MAX_CAPACITY) * FULL_CAPACITY
cc.SetSourceRGB(1.0, 1.0, 0.72)This code here, draws a yellow rectangle up to point, where the medium is full.
cc.Rectangle(0, 0, till, PANEL_HEIGHT)
cc.Clip
cc.Paint
cc.ResetClip
Dim extents As Cairo.TextExtents = cc.TextExtents(num(i-1))This code here draws the numbers on the burning widget. We calculate the TextExtents to position the text correctly.
cc.MoveTo(i*move-extents.Width/2, 15)
cc.TextPath(num(i-1))
cc.Stroke
burning.vb
' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThis is the main class.
'
' In this program, we create
' a custom widget
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
NameSpace Custom
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Const MAX_CAPACITY As Integer = 750
Dim cur_value As Integer
Dim burning As BurningWidget.Burning
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Burning")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(350, 200)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)
Dim scale As New HScale(0, MAX_CAPACITY, 1)
scale.SetSizeRequest(160, 35)
AddHandler scale.ValueChanged, AddressOf Me.OnChanged
Dim fixed As New Fixed
fixed.Put(scale, 50, 50)
vbox.PackStart(fixed)
burning = New BurningWidget.Burning(Me)
vbox.PackStart(burning, False, False, 0)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Private Sub OnChanged(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)
cur_value = sender.Value
burning.QueueDraw
End Sub
Public Function GetCurrentWidth As Integer
Return cur_value
End Function
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Private Sub OnChanged(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)We get the value from the scale widget, store it in the cur_value variable for later use. We redraw the burning widget.
cur_value = sender.Value
burning.QueueDraw
End Sub
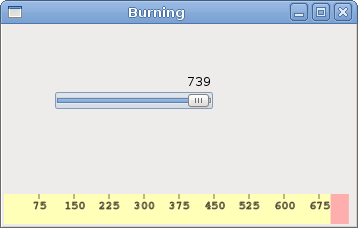
Figure: Burning widget
In this chapter, we created a custom widget in GTK# and Visual Basic.
Drawing with Cairo in Visual Basic GTK#
Drawing with Cairo
In this part of the Visual Basic GTK# tutorial, we will do some painting with the Cairo library.Cairo is a library for creating 2D vector graphics. We can use it to draw our own widgets, charts or various effects or animations.
Colors
In the first example, we will work with colors. A color is an object representing a combination of Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) intensity values. Cairo valid RGB values are in the range 0 to 1.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn our example, we will draw three rectangles and fill them with three different colors.
'
' This program draws three rectangles.
' The interiors are filled with
' different colors.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Colors")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(360, 100)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim darea As New DrawingArea
AddHandler darea.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExpose
Me.Add(darea)
End Sub
Private Sub OnExpose(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As ExposeEventArgs)
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)
Me.DrawColors(cc)
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)
disposeTarget.Dispose
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose
End Sub
Private Sub DrawColors(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
cc.SetSourceRGB(0.2, 0.23, 0.9)
cc.Rectangle(10, 15, 90, 60)
cc.Fill
cc.SetSourceRGB(0.9, 0.1, 0.1)
cc.Rectangle(130, 15, 90, 60)
cc.Fill
cc.SetSourceRGB(0.4, 0.9, 0.4)
cc.Rectangle(250, 15, 90, 60)
cc.Fill
End Sub
Private Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
vbnc -r:/usr/lib/mono/gtk-sharp-2.0/gtk-sharp.dllHere is how we compile the example.
-r:/usr/lib/mono/gtk-sharp-2.0/gdk-sharp.dll
-r:/usr/lib/mono/2.0/Mono.Cairo.dll colors.vb
Dim darea As New DrawingAreaWe will be doing our drawing operations on the DrawingArea widget.
AddHandler darea.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExposeAll drawing is done in a method, that we plug into the ExposeEvent.
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)We create the Cairo.Context object from the GdkWindow of the drawing area. The context is an object onto which we do all our drawings.
Me.DrawColors(cc)The actual drawing is delegated to the DrawColors method.
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)Here we dispose the resources, that were used during the drawing process.
disposeTarget.Dispose
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose
cc.SetSourceRGB(0.2, 0.23, 0.9)The SetSourceRGB method sets a color for the cairo context. The three parameters of the method are the color intensity values.
cc.Rectangle(10, 15, 90, 60)We draw a rectangle. The first two parameters are the x, y coordinates of the top left corner of the rectangle. The last two parameters are the width and height of the rectangle.
cc.FillWe fill the inside of the rectangle with the current color.
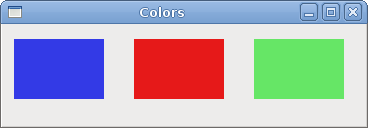
Figure: Colors
Basic shapes
The next example draws some basic shapes onto the window.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn this example, we will create a rectangle, a square, a circle, an arc and an ellipse.
'
' This program draws basic shapes
' available in Cairo
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Basic Shapes")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(400, 250)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim darea As New DrawingArea
AddHandler darea.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExpose
Me.Add(darea)
End Sub
Private Sub OnExpose(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As ExposeEventArgs)
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)
Me.DrawShapes(cc)
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)
disposeTarget.Dispose
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose
End Sub
Private Sub DrawShapes(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
cc.SetSourceRGB(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
cc.Rectangle(20, 20, 120, 80)
cc.Rectangle(180, 20, 80, 80)
cc.Fill
cc.Arc(330, 60, 40, 0, 2*Math.PI)
cc.Fill
cc.Arc(90, 160, 40, Math.PI/4, Math.PI)
cc.ClosePath
cc.Fill
cc.Translate(220, 180)
cc.Scale(1, 0.7)
cc.Arc(0, 0, 50, 0, 2*Math.PI)
cc.Fill
End Sub
Private Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
cc.Rectangle(20, 20, 120, 80)These lines draw a rectangle and a square.
cc.Rectangle(180, 20, 80, 80)
cc.Fill
cc.Arc(330, 60, 40, 0, 2*Math.PI)Here the Arc method draws a full circle.
cc.Fill
cc.Translate(220, 180)The Translate method moves the object to a specific point. If we want to draw an oval, we do some scaling first. Here the Scale method shrinks the y axis.
cc.Scale(1, 0.7)
cc.Arc(0, 0, 50, 0, 2*Math.PI)
cc.Fill
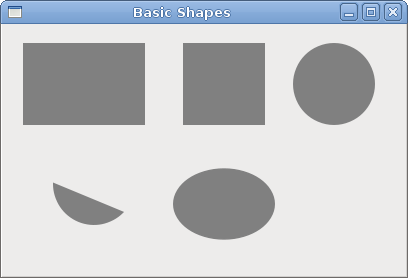
Figure: Basic shapes
Transparent rectangles
Transparency is the quality of being able to see through a material. The easiest way to understand transparency is to imagine a piece of glass or water. Technically, the rays of light can go through the glass and this way we can see objects behind the glass.In computer graphics, we can achieve transparency effects using alpha compositing. Alpha compositing is the process of combining an image with a background to create the appearance of partial transparency. The composition process uses an alpha channel. (wikipedia.org, answers.com)
' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn the example we will draw ten rectangles with different levels of transparency.
'
' This program draws ten
' rectangles with different
' levels of transparency
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Transparent rectangles")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(590, 90)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim darea As New DrawingArea
AddHandler darea.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExpose
Me.Add(darea)
End Sub
Private Sub OnExpose(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As ExposeEventArgs)
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)
Me.DrawRectangles(cc)
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)
disposeTarget.Dispose()
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose()
End Sub
Private Sub DrawRectangles(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
For i As Integer = 1 To 10
cc.SetSourceRGBA(0, 0, 1, i*0.1)
cc.Rectangle(50*i, 20, 40, 40)
cc.Fill
Next
End Sub
Private Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
cc.SetSourceRGBA(0, 0, 1, i*0.1)The last parameter of the SetSourceRGBA method is the alpha transparency.
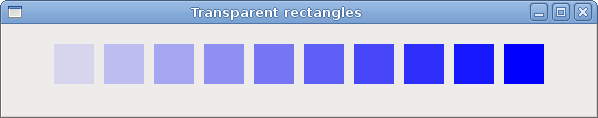
Figure: Transparent rectangles
Donut
In the following example we create n complex shape by rotating a bunch of ellipses.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn this example, we create a donut. The shape resembles a cookie, hence the name donut.
'
' This program draws basic shapes
' available in Cairo
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Donut")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(400, 250)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim darea As New DrawingArea
AddHandler darea.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExpose
Me.Add(darea)
End Sub
Private Sub OnExpose(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As ExposeEventArgs)
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)
Me.DrawDonut(cc)
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)
disposeTarget.Dispose
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose
End Sub
Private Sub DrawDonut(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
cc.LineWidth = 0.5
Dim width, height As Integer
width = Allocation.Width
height = Allocation.Height
cc.Translate(width/2, height/2)
cc.Arc(0, 0, 120, 0, 2*Math.PI)
cc.Stroke
cc.Save
For i As Integer = 0 To 35
cc.Rotate( i*Math.PI/36)
cc.Scale(0.3, 1)
cc.Arc(0, 0, 120, 0, 2*Math.PI)
cc.Restore
cc.Stroke
cc.Save
Next
End Sub
Private Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
cc.Translate(width/2, height/2)In the beginning there is an ellipse.
cc.Arc(0, 0, 120, 0, 2*Math.PI)
cc.Stroke
For i As Integer = 0 To 35After several rotations, there is a donut.
cc.Rotate( i*Math.PI/36)
cc.Scale(0.3, 1)
cc.Arc(0, 0, 120, 0, 2*Math.PI)
cc.Restore
cc.Stroke
cc.Save
Next
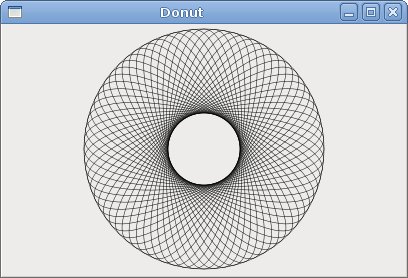
Figure: Donut
Drawing text
In the next example, we draw some text on the window.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialWe display part of the lyrics from the Natasha Bedingfields Soulmate song.
'
' This program draws text
' on the window
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Soulmate")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(400, 250)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim darea As New DrawingArea
AddHandler darea.ExposeEvent, AddressOf Me.OnExpose
Me.Add(darea)
End Sub
Private Sub OnExpose(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As ExposeEventArgs)
Dim cc As Cairo.Context = Gdk.CairoHelper.Create(sender.GdkWindow)
Me.DrawLyrics(cc)
Dim disposeTarget As IDisposable = CType(cc.Target, IDisposable)
disposeTarget.Dispose
Dim disposeContext As IDisposable = CType(cc, IDisposable)
disposeContext.Dispose
End Sub
Private Sub DrawLyrics(ByVal cc As Cairo.Context)
cc.SetSourceRGB(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)
cc.SelectFontFace("Purisa", Cairo.FontSlant.Normal, Cairo.FontWeight.Bold)
cc.SetFontSize(13)
cc.MoveTo(20, 30)
cc.ShowText("Most relationships seem so transitory")
cc.MoveTo(20, 60)
cc.ShowText("They're all good but not the permanent one")
cc.MoveTo(20, 120)
cc.ShowText("Who doesn't long for someone to hold")
cc.MoveTo(20, 150)
cc.ShowText("Who knows how to love without being told")
cc.MoveTo(20, 180)
cc.ShowText("Somebody tell me why I'm on my own")
cc.MoveTo(20, 210)
cc.ShowText("If there's a soulmate for everyone")
End Sub
Private Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
cc.SelectFontFace("Purisa", Cairo.FontSlant.Normal, Cairo.FontWeight.Bold)
Here we specify the font, that we use. Purisa bold. cc.SetFontSize(13)We specify the size of the font.
cc.MoveTo(20, 30)We move to the point, where we will draw the text.
cc.ShowText("Most relationships seem so transitory")
The ShowText method draws text onto the window. 
Figure: Soulmate
In this chapter of the Visual Basic GTK# tutorial, we were painting with Cairo library.
Dialogs in Visual Basic GTK#
Dialogs
In this part of the Visual Basic GTK# programming tutorial, we will introduce dialogs.Dialog windows or dialogs are an indispensable part of most modern GUI applications. A dialog is defined as a conversation between two or more persons. In a computer application a dialog is a window which is used to "talk" to the application. A dialog is used to input data, modify data, change the application settings etc. Dialogs are important means of communication between a user and a computer program.
Message boxes
Message dialogs are convenient dialogs that provide messages to the user of the application. The message consists of textual and image data.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn our example, we will show four kinds of message dialogs. Information, Warning, Question and Error message dialogs.
'
' This program shows message dialogs.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Message dialogs")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 100)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim table As New Table(2, 2, True)
Dim info As New Button("Information")
Dim warn As New Button("Warning")
Dim ques As New Button("Question")
Dim erro As New Button("Error")
AddHandler info.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnInfo
AddHandler warn.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnWarning
AddHandler ques.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnQuestion
AddHandler erro.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnError
table.Attach(info, 0, 1, 0, 1)
table.Attach(warn, 1, 2, 0, 1)
table.Attach(ques, 0, 1, 1, 2)
table.Attach(erro, 1, 2, 1, 2)
Me.Add(table)
End Sub
Private Sub OnInfo(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim md As MessageDialog = New MessageDialog(Me, _
DialogFlags.DestroyWithParent, MessageType.Info, _
ButtonsType.Close, "Download completed")
md.Run
md.Destroy
End Sub
Private Sub OnWarning(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim md As MessageDialog = New MessageDialog(Me, _
DialogFlags.DestroyWithParent, MessageType.Warning, _
ButtonsType.Close, "Unallowed operation")
md.Run
md.Destroy
End Sub
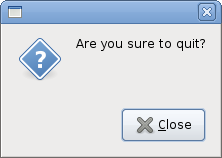
Private Sub OnQuestion(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim md As MessageDialog = New MessageDialog(Me, _
DialogFlags.DestroyWithParent, MessageType.Question, _
ButtonsType.Close, "Are you sure to quit?")
md.Run
md.Destroy
End Sub
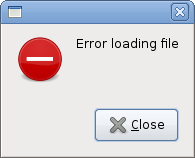
Private Sub OnError(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim md As MessageDialog = New MessageDialog(Me, _
DialogFlags.DestroyWithParent, MessageType.Error, _
ButtonsType.Close, "Error loading file")
md.Run
md.Destroy
End Sub
Private Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim info As New Button("Information")
Dim warn As New Button("Warning")
Dim ques As New Button("Question")
Dim erro As New Button("Error")
We have four buttons. Each of these buttons will show a different kind of message dialog. Private Sub OnInfo(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)If we click on the info button, the Information dialog is displayed. The MessageType.Info specifies the type of the dialog. The ButtonsType.Close specifies the button to be displayed in the dialog. The last parameter is the message dislayed. The dialog is displayed with the Run method. The programmer must also call either the Destroy or the Hide method.
Dim md As MessageDialog = New MessageDialog(Me, _
DialogFlags.DestroyWithParent, MessageType.Info, _
ButtonsType.Close, "Download completed")
md.Run
md.Destroy
End Sub
AboutDialog
The AboutDialog displays information about the application. AboutDialogcan display a logo, the name of the application, version, copyright, website or licence information. It is also possible to give credits to the authors, documenters, translators and artists.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThe code example uses a AboutDialog with some of its features.
'
' This program shows the about
' dialog
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("About dialog")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(350, 300)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim button As New Button("About")
AddHandler button.Clicked, AddressOf Me.ShowDialog
Dim fixed As New Fixed
fixed.Put(button, 20, 20)
Me.Add(fixed)
End Sub
Private Sub ShowDialog(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim about As New AboutDialog
about.ProgramName = "Battery"
about.Version = "0.1"
about.Copyright = "(c) Jan Bodnar"
about.Comments = "Battery is a simple tool for battery checking"
about.Website = "http://www.zetcode.com"
about.Logo = New Gdk.Pixbuf("battery.png")
about.Run
about.Destroy
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim about As New AboutDialogWe create an AboutDialog.
Dim about As New AboutDialogBy setting the properties of the dialog, we specify the name, version and the copyright.
about.ProgramName = "Battery"
about.Version = "0.1"
about.Copyright = "(c) Jan Bodnar"
about.Logo = New Gdk.Pixbuf("battery.png")
This line creates a logo. 
Figure: AboutDialog
FontSelectionDialog
The FontSelectionDialog is a dialog for selecting fonts. It is typically used in applications, that do some text editing or formatting.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn the code example, we have a button and a label. We show the FontSelectionDialog by clicking on the button.
'
' This program shows the FontSelectionDialog
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Dim label As Label
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Font dialog")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(350, 300)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
label = New Label("The only victory over love is flight.")
Dim button As New Button("Select font")
AddHandler button.Clicked, AddressOf Me.ShowDialog
Dim fixed As New Fixed
fixed.Put(button, 100, 30)
fixed.Put(label, 30, 90)
Me.Add(fixed)
End Sub
Private Sub ShowDialog(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim fdia As New FontSelectionDialog("Select font name")
AddHandler fdia.Response, AddressOf Me.SelectFont
fdia.Run
fdia.Destroy
End Sub
Private Sub SelectFont(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As ResponseArgs)
If args.ResponseId = ResponseType.Ok
Dim fontdesc As Pango.FontDescription = _
Pango.FontDescription.FromString(sender.FontName)
label.ModifyFont(fontdesc)
End If
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim fdia As New FontSelectionDialog("Select font name")
We create the FontSelectionDialog. If args.ResponseId = ResponseType.OkIf we click on the OK button, the font of the label widget changes to the one, that we selected in the dialog.
Dim fontdesc As Pango.FontDescription = _
Pango.FontDescription.FromString(sender.FontName)
label.ModifyFont(fontdesc)
End If
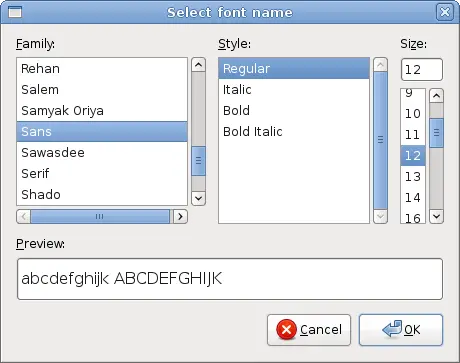
Figure: FontSelectionDialog
ColorSelectionDialog
ColorSelectionDialog is a dialog for selecting a color.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThe example is very similar to the previous one. This time we change the color of the label.
'
' This program shows the ColorSelectionDialog
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Dim label As Label
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Color dialog")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(350, 300)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
label = New Label("The only victory over love is flight.")
Dim button As New Button("Select color")
AddHandler button.Clicked, AddressOf Me.ShowDialog
Dim fixed As New Fixed
fixed.Put(button, 100, 30)
fixed.Put(label, 30, 90)
Me.Add(fixed)
End Sub
Private Sub ShowDialog(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim cdia As New ColorSelectionDialog("Select color")
AddHandler cdia.Response, AddressOf Me.SelectColor
cdia.Run
cdia.Destroy
End Sub
Private Sub SelectColor(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As ResponseArgs)
If args.ResponseId = ResponseType.Ok
label.ModifyFg(StateType.Normal, _
sender.ColorSelection.CurrentColor)
End If
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim cdia As New ColorSelectionDialog("Select color")
We create the ColorSelectionDialog. If args.ResponseId = ResponseType.OkIf the user pressed OK, we get the color value and modify the label's color.
label.ModifyFg(StateType.Normal, _
sender.ColorSelection.CurrentColor)
End If
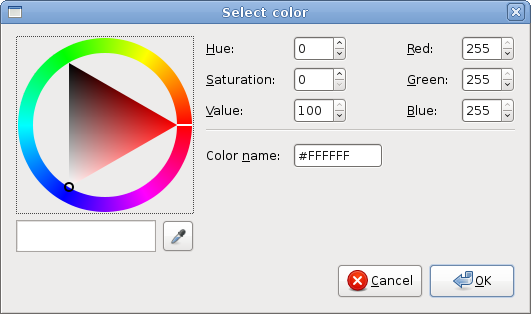
Figure: ColorSelectionDialog
In this part of the Visual Basic GTK# tutorial, we presented dialogs.
Menus And toolbars in Visual Basic GTK#
Menus And toolbars
In this part of the Visual Basic GTK# programming tutorial, we will work with menus & toolbars.A menubar is one of the most common parts of the GUI application. It is a group of commands located in various menus. While in console applications you have to remember all those arcane commands, here we have most of the commands grouped into logical parts. These are accepted standards that further reduce the amount of time spending to learn a new application.
Simple menu
In our first example, we will create a menubar with one file menu. The menu will have only one menu item. By selecting the item the application quits.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThis is a small example with minimal menubar functionality.
'
' This program shows a simple
' menu. It has one action, which
' will terminate the program, when
' selected.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Simple menu")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 200)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim mb As New MenuBar
Dim filemenu As New Menu
Dim fileItem As New MenuItem("File")
fileItem.Submenu = filemenu
Dim exitItem As New MenuItem("Exit")
AddHandler exitItem.Activated, AddressOf Me.OnActivated
filemenu.Append(exitItem)
mb.Append(fileItem)
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)
vbox.PackStart(mb, False, False, 0)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Sub OnActivated(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim mb As New MenuBarMenuBar widget is created. This is a container for the menus.
Dim filemenu As New MenuToplevel MenuItem is created.
Dim fileItem As New MenuItem("File")
fileItem.Submenu = filemenu
Dim exitItem As New MenuItem("Exit")
AddHandler exitItem.Activated, AddressOf Me.OnActivated
filemenu.Append(exitItem)
Exit MenuItem is created and appended to the File MenuItem. mb.Append(fileItem)Toplevel MenuItem is appended to the MenuBarwidget.
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)Unlike in other toolkits, we have to take care of the layout management of the menubar ourselves. We put the menubar into the vertical box.
vbox.PackStart(mb, False, False, 0)
Figure: Simple menu
Submenu
Our final example demonstrates how to create a submenu in GTK#.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialSubmenu creation.
'
' This program creates a submenu
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Submenu")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 200)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim mb As New MenuBar
Dim filemenu As New Menu
Dim ifile As New MenuItem("File")
ifile.Submenu = filemenu
// submenu creation
Dim imenu As New Menu
Dim iimport As New MenuItem("Import")
iimport.Submenu = imenu
Dim inews As New MenuItem("Import news feed...")
Dim ibookmarks As New MenuItem("Import bookmarks...")
Dim imail As New MenuItem("Import mail...")
imenu.Append(inews)
imenu.Append(ibookmarks)
imenu.Append(imail)
// exit menu item
Dim iexit As New MenuItem("Exit")
AddHandler iexit.Activated, AddressOf Me.OnActivated
filemenu.Append(iimport)
filemenu.Append(iexit)
mb.Append(ifile)
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)
vbox.PackStart(mb, False, False, 0)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Sub OnActivated(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim imenu As New MenuA submenu is a Menu.
Dim iimport As New MenuItem("Import")
iimport.Submenu = imenu
It is a submenu of a menu item, which belogs to toplevel file menu. Dim inews As New MenuItem("Import news feed...")
Dim ibookmarks As New MenuItem("Import bookmarks...")
Dim imail As New MenuItem("Import mail...")
imenu.Append(inews)
imenu.Append(ibookmarks)
imenu.Append(imail)
Submenu has its own menu items. 
Figure: Submenu
Image menu
In the next example, we will further explore the menus. We will add images and accelerators to our menu items. Accelerators are keyboard shortcuts for activating a menu item.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialOur example shows a toplevel menu item with three sublevel menu items. Each of the menu items has a image and an accelerator. The accelerator for the quit menu item is active.
'
' This program shows image
' menu items, a shorcut and a separator
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Image menu")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 200)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim mb As New MenuBar
Dim filemenu As New Menu
Dim ifile As New MenuItem("File")
ifile.Submenu = filemenu
Dim agr As New AccelGroup
Me.AddAccelGroup(agr)
Dim inew As New ImageMenuItem("gtk-new", agr)
filemenu.Append(inew)
Dim iopen As New ImageMenuItem(Stock.Open, agr)
filemenu.Append(iopen)
Dim isep As New SeparatorMenuItem
filemenu.Append(isep)
Dim iexit As New ImageMenuItem(Stock.Quit, agr)
AddHandler iexit.Activated, AddressOf Me.OnActivated
filemenu.Append(iexit)
mb.Append(ifile)
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)
vbox.PackStart(mb, False, False, 0)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Sub OnActivated(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim agr As New AccelGroupTo work with accelerators, we create a global AccelGroupobject. It will be used later.
Me.AddAccelGroup(agr)
Dim inew As New ImageMenuItem("gtk-new", agr)
filemenu.Append(inew)
ImageMenuItem is created. The image comes from the stock of images. There is a bug in the GTK#. The Stock.New clashes with the Visual Basic New keyword. Dim isep As New SeparatorMenuItemThese lines create a separator. It is used to put menu items into logical groups.
filemenu.Append(isep)
Figure: Image menu
Menus group commands that we can use in application. Toolbars provide a quick access to the most frequently used commands.
Simple toolbar
Next we create a simple toolbar.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThe example shows a toolbar and four tool buttons.
'
' This program creates a
' toolbar
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Toolbar")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 200)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim toolbar As New Toolbar
toolbar.ToolbarStyle = ToolbarStyle.Icons
Dim newtb As New ToolButton("gtk-new")
Dim opentb As New ToolButton(Stock.Open)
Dim savetb As New ToolButton(Stock.Save)
Dim sep As New SeparatorToolItem
Dim quittb As New ToolButton(Stock.Quit)
toolbar.Insert(newtb, 0)
toolbar.Insert(opentb, 1)
toolbar.Insert(savetb, 2)
toolbar.Insert(sep, 3)
toolbar.Insert(quittb, 4)
AddHandler quittb.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnClicked
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)
vbox.PackStart(toolbar, False, False, 0)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Sub OnClicked(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim toolbar As New ToolbarA Toolbar widget is created.
toolbar.ToolbarStyle = ToolbarStyle.IconsOn toolbar, we show only icons. No text.
Dim opentb As New ToolButton(Stock.Open)A ToolButton with an image from stock is created.
Dim sep As New SeparatorToolItemThis is a separator. It can be used to put toolbar buttons into logical groups.
toolbar.Insert(newtb, 0)Toolbar buttons are inserted into the toolbar widget.
toolbar.Insert(opentb, 1)
...
Figure: Toolbar
Undo redo
The following example demonstrates, how we can deactivate toolbar buttons on the toolbar. It is a common practise in GUI programming. For example the save button. If we save all changes of our document to the disk, the save button is deactivated in most text editors. This way the application indicates to the user, that all changes are already saved.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialOur example creates undo and redo buttons from the GTK# stock resources. After several clicks each of the buttons is deactivated. The buttons are grayed out.
'
' This program disables/enables
' toolbuttons on a toolbar
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Private Dim clicks As Integer = 2
Private Dim undo As ToolButton
Private Dim redo As ToolButton
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Undo redo")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 200)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim toolbar As New Toolbar
toolbar.ToolbarStyle = ToolbarStyle.Icons
undo = New ToolButton(Stock.Undo)
undo.Label = "Undo"
redo = New ToolButton(Stock.Redo)
redo.Label = "Redo"
Dim sep As New SeparatorToolItem
Dim quit As New ToolButton(Stock.Quit)
toolbar.Insert(undo, 0)
toolbar.Insert(redo, 1)
toolbar.Insert(sep, 2)
toolbar.Insert(quit, 3)
AddHandler undo.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnCount
AddHandler redo.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnCount
AddHandler quit.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnClicked
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)
vbox.PackStart(toolbar, False, False, 0)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Private Sub OnCount(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
If "Undo".Equals(sender.Label)
clicks += 1
Else
clicks -= 1
End If
If clicks <= 0
undo.Sensitive = True
redo.Sensitive = False
End If
If clicks >= 5
undo.Sensitive = False
redo.Sensitive = True
End If
End Sub
Sub OnClicked(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Private Dim clicks As Integer = 2The clicks variable decides, which button is activated or deactivated.
undo = New ToolButton(Stock.Undo)We have two tool buttons. Undo and redo tool buttons. Images come from the stock resources.
undo.Label = "Undo"
redo = New ToolButton(Stock.Redo)
redo.Label = "Redo"
AddHandler undo.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnCountWe plug a method for the Clicked event for both tool buttons.
AddHandler redo.Clicked, AddressOf Me.OnCount
If clicks <= 0To activate a widget, we set its Sensitive property to true. To deactivate it, we set it to false.
undo.Sensitive = True
redo.Sensitive = False
End If
Figure: Undo redo
In this chapter of the Visual Basic GTK# tutorial, we showed, how to work with menus & toolbars.
Widgets in Visual Basic GTK#
Widgets
In this part of the Visual Basic GTK# programming tutorial, we will introduce some widgets.Widgets are basic building blocks of a GUI application. Over the years, several widgets became a standard in all toolkits on all OS platforms. For example a button, a check box or a scroll bar. The GTK# toolkit's philosophy is to keep the number of widgets at a minimum level. More specialized widgets are created as custom GTK# widgets.
CheckButton
CheckButton is a widget, that has two states. On and Off. The On state is visualised by a check mark. It is used to denote some boolean property.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialWe will display a title in the titlebar of the window, depending on the state of the CheckButton.
'
' This program toggles the title of the
' window with the CheckButton widget
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("CheckButton")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 150)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim cb As New CheckButton("Show title")
cb.Active = True
AddHandler cb.Toggled, AddressOf Me.OnToggle
Dim fix As New Fixed
fix.Put(cb, 50, 50)
Me.Add(fix)
End Sub
Sub OnToggle(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As EventArgs)
If sender.Active
Me.Title = "CheckButton"
Else
Title = " "
End If
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim cb As New CheckButton("Show title")
CheckButton widget is created. cb.Active = TrueThe title is visible by default, so we check the check button by default.
If sender.ActiveDepending on the Active property of the CheckButton, we show or hide the title of the window.
Me.Title = "CheckButton"
Else
Title = " "
End If
Figure: CheckButton
Label
The Label widget shows text.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThe code example shows some lyrics on the window.
' This program shows lyrics on
' the window in a label widget
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Dim text As String = "Meet you downstairs in the bar and heard" & vbNewLine & _
"your rolled up sleeves and your skull t-shirt" & vbNewLine & _
"You say why did you do it with him today?" & vbNewLine & _
"and sniff me out like I was Tanqueray" & vbNewLine & _
"" & vbNewLine & _
"cause you're my fella, my guy" & vbNewLine & _
"hand me your stella and fly" & vbNewLine & _
"by the time I'm out the door" & vbNewLine & _
"you tear men down like Roger Moore" & vbNewLine & _
"" & vbNewLine & _
"I cheated myself" & vbNewLine & _
"like I knew I would" & vbNewLine & _
"I told ya, I was trouble" & vbNewLine & _
"you know that I'm no good"
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("You know I'm No Good")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
Me.BorderWidth = 10
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim lyrics As New Label(text)
Me.Add(lyrics)
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim text As String = "Meet you downstairs in the bar and heard" & vbNewLine & _We define a multi line text. Unlike in C#, Python or Ruby, there is no simple construct to create a multi line text in Visual Basic language. To create a multi line text in Visual Basic, we use the vbNewLineprint constant, the + concatenation character and the _ line termination character.
"your rolled up sleeves and your skull t-shirt" & vbNewLine & _
...
Me.BorderWidth = 10The Label is surrounded by some empty space.
Dim lyrics As New Label(text)The Label widget is created and added to the window.
Me.Add(lyrics)

Figure: Label Widget
Entry
The Entry is a single line text entry field. This widget is used to enter textual data.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThis example shows an entry widget and a label. The text that we key in the entry is displayed immediately in the label widget.
'
' This program demonstrates the
' Entry widget. Text entered in the Entry
' widget is shown in a Label widget.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Dim label As Label
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Entry")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(250, 150)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim fixed As New Fixed
label = New Label("...")
fixed.put(label, 60, 40)
Dim entry As New Entry
fixed.put(entry, 60, 100)
AddHandler entry.Changed, AddressOf Me.OnTextChanged
Me.Add(fixed)
End Sub
Sub OnTextChanged(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
label.Text = sender.Text
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim entry As New EntryEntry widget is created.
AddHandler entry.Changed, AddressOf Me.OnTextChangedIf the text in the Entry widget is changed, we call the OnTextChanged method.
Sub OnTextChanged(ByVal sender As Object, _We get the text from the Entry widget and set it to the label.
ByVal args As EventArgs)
label.Text = sender.Text
End Sub
Figure: Entry Widget
ToggleButton
ToggleButton is a button that has two states. Pressed and not pressed. You toggle between these two states by clicking on it. There are situations where this functionality fits well.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn our example, we show three toggle buttons and a DrawingArea. We set the background color of the area to black. The togglebuttons will toggle the red, green and blue parts of the color value. The background color will depend on which togglebuttons we have pressed.
'
' This program uses toggle buttons to
' change the background color of
' a widget.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Dim darea As DrawingArea
Dim color As Gdk.Color
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Togggle buttons")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(350, 240)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
color = New Gdk.Color(0, 0, 0)
Dim redb As New ToggleButton("Red")
redb.SetSizeRequest(80, 35)
AddHandler redb.Toggled, AddressOf Me.OnToggled
Dim greenb As New ToggleButton("Green")
greenb.SetSizeRequest(80, 35)
AddHandler greenb.Toggled, AddressOf Me.OnToggled
Dim blueb As New ToggleButton("Blue")
blueb.SetSizeRequest(80, 35)
AddHandler blueb.Toggled, AddressOf Me.OnToggled
darea = New DrawingArea
darea.SetSizeRequest(150, 150)
darea.ModifyBg(StateType.Normal, color)
Dim fixed As New Fixed
fixed.Put(redb, 30, 30)
fixed.Put(greenb, 30, 80)
fixed.Put(blueb, 30, 130)
fixed.Put(darea, 150, 30)
Me.Add(fixed)
End Sub
Private Sub OnToggled(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
Dim red As Integer = color.Red
Dim green As Integer = color.Green
Dim blue As Integer = color.Blue
If sender.Label.Equals("Red")
If sender.Active
color.Red = 65535
Else
color.Red = 0
End If
End If
If sender.Label.Equals("Green")
If sender.Active
color.Green = 65535
Else
color.Green = 0
End If
End If
If sender.Label.Equals("Blue")
If sender.Active
color.Blue = 65535
Else
color.Blue = 0
End If
End If
darea.ModifyBg(StateType.Normal, color)
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
color = New Gdk.Color(0, 0, 0)This is the color value that is going to be updated with the toggle buttons.
Dim redb As New ToggleButton("Red")
redb.SetSizeRequest(80, 35)
AddHandler redb.Toggled, AddressOf Me.OnToggled
The ToggleButton widget is created. We set it's size to 80x35 pixels. Each of the toggle buttons has the same handler method. darea = New DrawingAreaThe DrawingArea widget is the widget, that displays the color, mixed by the toggle buttons. At start, it shows black color.
darea.SetSizeRequest(150, 150)
darea.ModifyBg(StateType.Normal, color)
If sender.Label.Equals("Red")
If sender.Active
color.Red = 65535
Else
color.Red = 0
End If
End If
We update the red part of the color according to the value of the Active property. darea.ModifyBg(StateType.Normal, color)We update the color of the DrawingArea widget.
Figure: ToggleButton widget
ComboBox
ComboBox is a widget that allows the user to choose from a list of options.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThe example shows a combo box and a label. The combo box has a list of six options. These are the names of Linux Distros. The label widget shows the selected option from the combo box.
'
' In this program, we use the ComboBox
' widget to select an option.
' The selected option is shown in the
' Label widget
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Dim lbl As Label
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("ComboBox")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(350, 240)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim distros() As String = New String() { _
"Ubuntu", _
"Mandriva", _
"Red Hat", _
"Fedora", _
"Gentoo" _
}
Dim fixed As New Fixed
Dim cb As New ComboBox(distros)
AddHandler cb.Changed, AddressOf Me.OnChanged
lbl = New Label("...")
fixed.Put(cb, 50, 40)
fixed.Put(lbl, 50, 140)
Me.Add(fixed)
End Sub
Private Sub OnChanged(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As EventArgs)
lbl.Text = sender.ActiveText
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim distros() As String = New String() { _
"Ubuntu", _
"Mandriva", _
"Red Hat", _
"Fedora", _
"Gentoo" _
}
This is an array of strings, that will be shown in the ComboBox widget. Dim cb As New ComboBox(distros)The ComboBox widget is created. The constructor takes the array of strings as a parameter.
Private Sub OnChanged(ByVal sender As Object, _Inside the OnChanged method, we get the selected text out of the combo box and set it to the label.
ByVal args As EventArgs)
lbl.Text = sender.ActiveText
End Sub
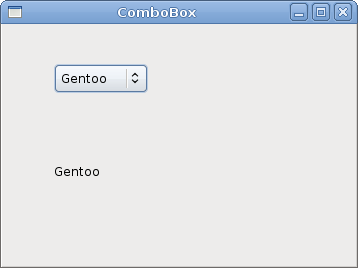
Figure: ComboBox
In this chapter, we showed some basic widgets of the GTK# programming library with the Visual Basic language.
Layout management in Visual Basic GTK#
Layout management
In this chapter we will show how to lay out our widgets in windows or dialogs.When we design the GUI of our application, we decide what widgets we will use and how we will organize those widgets in the application. To organize our widgets, we use specialized non visible widgets called layout containers. In this chapter, we will mention Alignment, Fixed, VBox and Table.
Fixed
The Fixed container places child widgets at fixed positions and with fixed sizes. This container performs no automatic layout management. In most applications, we don't use this container. There are some specialized areas, where we use it. For example games, specialized applications that work with diagrams, resizable components that can be moved (like a chart in a spreadsheet application), small educational examples.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn our example, we show three small images on the window. We explicitly specify the x, y coordinates, where we place these images.
'
' In this program, we lay out widgets
' using absolute positioning
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Private Dim rotunda As Gdk.Pixbuf
Private Dim bardejov As Gdk.Pixbuf
Private Dim mincol As Gdk.Pixbuf
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Fixed")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(300, 280)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Me.ModifyBg(StateType.Normal, New Gdk.Color(40, 40, 40))
Try
bardejov = New Gdk.Pixbuf("bardejov.jpg")
rotunda = New Gdk.Pixbuf("rotunda.jpg")
mincol = New Gdk.Pixbuf("mincol.jpg")
Catch e As Exception
Console.WriteLine("Cannot load images")
Console.WriteLine(e.Message)
Environment.Exit(1)
End Try
Dim image1 As New Image(bardejov)
Dim image2 As New Image(rotunda)
Dim image3 As New Image(mincol)
Dim fixed As New Fixed
fixed.Put(image1, 20, 20)
fixed.Put(image2, 40, 160)
fixed.Put(image3, 170, 50)
Me.Add(fixed)
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
vbnc -r:/usr/lib/mono/gtk-sharp-2.0/gtk-sharp.dll -r:/usr/lib/mono/gtk-sharp-2.0/gdk-sharp.dllWe also use the gdk-sharp assembly in this example.
absolute.vb
Me.ModifyBg(StateType.Normal, New Gdk.Color(40, 40, 40))For better visual experience, we change the background color to dark gray.
bardejov = New Gdk.Pixbuf("bardejov.jpg")
We load the image from the disk to the Gdk.Pixbuf object. Dim image1 As New Image(bardejov)The Image is a widget, that is used to display images. It takes Gdk.Pixbuf object in the constructor.
Dim image2 As New Image(rotunda)
Dim image3 As New Image(mincol)
Dim fixed As New FixedWe create the Fixed container.
fixed.Put(image1, 20, 20)We place the first image at x=20, y=20 coordinates.
Me.Add(fixed)Finally, we add the Fixed container to the Window.
Figure: Fixed
Buttons
The Alignment container controls the alignment and the size of its child widget.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialIn the code example, we place two buttons into the right bottom corner of the window. To accomplish this, we use one horizontal box and one vertical box and two alignment containers.
'
' In this program, we position two buttons
' in the bottom right corner of the window.
' We use horizontal and vertical boxes.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Buttons")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(260, 150)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 5)
Dim hbox As New HBox(True, 3)
Dim valign As New Alignment(0, 1, 0, 0)
vbox.PackStart(valign)
Dim ok As New Button("OK")
ok.SetSizeRequest(70, 30)
Dim close As New Button("Close")
hbox.Add(ok)
hbox.Add(close)
Dim halign As New Alignment(1, 0, 0, 0)
halign.Add(hbox)
vbox.PackStart(halign, False, False, 3)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim valign As New Alignment(0, 1, 0, 0)This will put the child widget to the bottom.
vbox.PackStart(valign)Here we place the Alignment widget into the vertical box.
Dim hbox As New HBox(True, 3)We create a horizontal box and put two buttons inside it.
...
Dim ok As New Button("OK")
ok.SetSizeRequest(70, 30)
Dim close As New Button("Close")
hbox.Add(ok)
hbox.Add(close)
Dim halign As New Alignment(1, 0, 0, 0)This will create an alignment container that will place its child widget to the right. We add the horizontal box into the alignment container and pack the alignment container into the vertical box. We must keep in mind that the alignment container takes only one child widget. That's why we must use boxes.
halign.Add(hbox)
vbox.PackStart(halign, False, False, 3)
Figure: Buttons
Calculator skeleton
The Table widget arranges widgets in rows and columns.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialWe use the Table widget to create a calculator skeleton.
'
' In this program we create a skeleton of
' a calculator. We use the Table widget.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Calculator")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(300, 250)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Dim vbox As New VBox(False, 2)
Dim mb As New MenuBar
Dim filemenu As New Menu
Dim file As MenuItem = New MenuItem("File")
file.Submenu = filemenu
mb.Append(file)
vbox.PackStart(mb, False, False, 0)
Dim table As New Table(5, 4, True)
table.Attach(New Button("Cls"), 0, 1, 0, 1)
table.Attach(New Button("Bck"), 1, 2, 0, 1)
table.Attach(New Label(), 2, 3, 0, 1)
table.Attach(New Button("Close"), 3, 4, 0, 1)
table.Attach(New Button("7"), 0, 1, 1, 2)
table.Attach(New Button("8"), 1, 2, 1, 2)
table.Attach(New Button("9"), 2, 3, 1, 2)
table.Attach(New Button("/"), 3, 4, 1, 2)
table.Attach(New Button("4"), 0, 1, 2, 3)
table.Attach(New Button("5"), 1, 2, 2, 3)
table.Attach(New Button("6"), 2, 3, 2, 3)
table.Attach(New Button("*"), 3, 4, 2, 3)
table.Attach(New Button("1"), 0, 1, 3, 4)
table.Attach(New Button("2"), 1, 2, 3, 4)
table.Attach(New Button("3"), 2, 3, 3, 4)
table.Attach(New Button("-"), 3, 4, 3, 4)
table.Attach(New Button("0"), 0, 1, 4, 5)
table.Attach(New Button("."), 1, 2, 4, 5)
table.Attach(New Button("="), 2, 3, 4, 5)
table.Attach(New Button("+"), 3, 4, 4, 5)
vbox.PackStart(New Entry, False, False, 0)
vbox.PackEnd(table, True, True, 0)
Me.Add(vbox)
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim table As New Table(5, 4, True)We create a table widget with 5 rows and 4 columns. The third parameter is the homogenous parameter. If set to true, all the widgets in the table are of same size. The size of all widgets is equal to the largest widget in the table container.
table.Attach(New Button("Cls"), 0, 1, 0, 1)
We attach a button to the table container. To the top-left cell of the table. The first two parameters are the left and right sides of the cell, the last two parameters are the top and left sides of the cell. vbox.PackEnd(table, True, True, 0)We pack the table widget into the vertical box.
Figure: Calculator skeleton
Windows
Next we will create a more advanced example. We show a window, that can be found in the JDeveloper IDE.' ZetCode Mono Visual Basic GTK# tutorialThe code example shows, how we can create a similar window in GTK#.
'
' This is a more complicated layout example.
' We use Alignment and Table widgets.
'
' author jan bodnar
' last modified May 2009
' website www.zetcode.com
Imports Gtk
Public Class GtkVBApp
Inherits Window
Public Sub New
MyBase.New("Windows")
Me.InitUI
Me.SetDefaultSize(300, 250)
Me.SetPosition(WindowPosition.Center)
AddHandler Me.DeleteEvent, AddressOf Me.OnDelete
Me.ShowAll
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI
Me.BorderWidth = 15
Dim table As New Table(8, 4, False)
table.ColumnSpacing = 3
Dim title As New Label("Windows")
Dim halign As New Alignment(0, 0, 0, 0)
halign.Add(title)
table.Attach(halign, 0, 1, 0, 1, AttachOptions.Fill, _
AttachOptions.Fill, 0, 0)
Dim frame As New Frame
table.Attach(frame, 0, 2, 1, 3, AttachOptions.Fill Or AttachOptions.Expand, _
AttachOptions.Fill Or AttachOptions.Expand, 1, 1)
Dim activate As New Button("Activate")
activate.SetSizeRequest(50, 30)
table.Attach(activate, 3, 4, 1, 2, AttachOptions.Fill, _
AttachOptions.Shrink, 1, 1)
Dim valign As New Alignment(0, 0, 0, 0)
Dim close As New Button("Close")
close.SetSizeRequest(70, 30)
valign.Add(close)
table.SetRowSpacing(1, 3)
table.Attach(valign, 3, 4, 2, 3, AttachOptions.Fill, _
AttachOptions.Fill Or AttachOptions.Expand, 1, 1)
Dim halign2 As New Alignment(0, 1, 0, 0)
Dim help As New Button("Help")
help.SetSizeRequest(70, 30)
halign2.Add(help)
table.SetRowSpacing(3, 6)
table.Attach(halign2, 0, 1, 4, 5, AttachOptions.Fill, _
AttachOptions.Fill, 0, 0)
Dim ok As New Button("OK")
ok.SetSizeRequest(70, 30)
table.Attach(ok, 3, 4, 4, 5, AttachOptions.Fill, _
AttachOptions.Fill, 0, 0)
Me.Add(table)
End Sub
Sub OnDelete(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal args As DeleteEventArgs)
Application.Quit
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main
Application.Init
Dim app As New GtkVBApp
Application.Run
End Sub
End Class
Dim table As New Table(8, 4, False)The example is based on the Table container. There will be 3px space between columns.
table.ColumnSpacing = 3
Dim title As New Label("Windows")
Dim halign As New Alignment(0, 0, 0, 0)
halign.Add(title)
table.Attach(halign, 0, 1, 0, 1, AttachOptions.Fill, _
AttachOptions.Fill, 0, 0)
This code creates a label, that is aligned to the left. The label is placed in the first row of the Table container. Dim frame As New FrameThe frame view widget spans two rows and two columns. We make the widget non editable and hide the cursor.
table.Attach(frame, 0, 2, 1, 3, AttachOptions.Fill Or AttachOptions.Expand, _
AttachOptions.Fill Or AttachOptions.Expand, 1, 1)
Dim valign As New Alignment(0, 0, 0, 0)We put the close button next to the frame widget into the fourth column. (we count from zero) We add the button into the alignment widget, so that we can align it to the top.
Dim close As New Button("Close")
close.SetSizeRequest(70, 30)
valign.Add(close)
table.SetRowSpacing(1, 3)
table.Attach(valign, 3, 4, 2, 3, AttachOptions.Fill, _
AttachOptions.Fill Or AttachOptions.Expand, 1, 1)
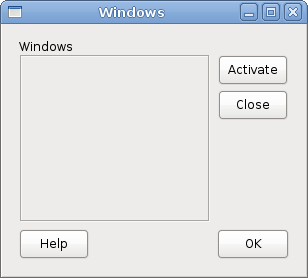
Figure: Windows
In this part of the Visual Basic GTK# tutorial, we mentioned layout management of widgets.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)