Layout management in Tk
In this part of the Tcl/Tk programming tutorial, we will introduce layout managers.When we design the GUI of our application, we decide what widgets we will use and how we will organize those widgets in the application. To organize our widgets, we use specialized non visible objects called layout managers.
There are two kinds of widgets. Containers and their children. The containers group their children into suitable layouts.
Tk has three built-in layout managers. The pack, grid and place managers. The pack geometry manager organizes widgets in vertical and horizontal boxes. The grid geometry managers places widgets in a two dimensional grid. Finally, the place geometry manager places widgets on their containers using absolute positioning.
Absolute positioning
In most cases, programmers should use layout managers. There are a few situations, where we can use absolute positioning. In absolute positioning, the programmer specifies the position and the size of each widget in pixels. The size and the position of a widget do not change, if you resize a window. Applications look different on various platforms, and what looks OK on Linux, might not look OK on Mac. Changing fonts in your application might spoil the layout. If you translate your application into another language, you must redo your layout.#!/usr/bin/wishIn this example, we place three images using absolute positioning. We will use the place geometry manager.
# ZetCode Tcl/Tk tutorial
#
# In this script, we lay out images
# using absolute positioning.
#
# author: Jan Bodnar
# last modified: March 2011
# website: www.zetcode.com
package require Img
frame .fr -background "#333"
pack .fr -fill both -expand 1
image create photo img1 -file "bardejov.jpg"
label .fr.lbl1 -image img1
place .fr.lbl1 -x 20 -y 20
image create photo img2 -file "rotunda.jpg"
label .fr.lbl2 -image img2
place .fr.lbl2 -x 40 -y 160
image create photo img3 -file "mincol.jpg"
label .fr.lbl3 -image img3
place .fr.lbl3 -x 170 -y 50
wm title . "absolute"
wm geometry . 300x280+300+300
package require ImgWe use the Img package to display jpg images. On Ubuntu we must install the libtk-img package.
package require ImgTo display jpg images, we use the Img package.
frame .fr -background "#333"Our frame will have a dark gray background.
image create photo img1 -file "bardejov.jpg"We create a photo image object from an image in the current working directory.
label .fr.lbl1 -image img1We create a
label with an image. Labels can contain text or images. place .fr.lbl1 -x 20 -y 20The label is placed on the frame at x=20, y=20 coordinates. Absolute positioning is done with the
place command. 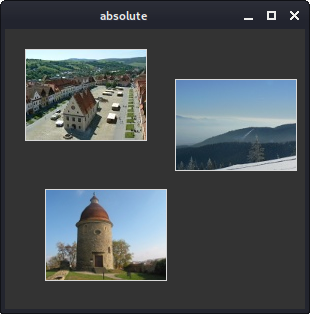
Figure: Absolute positioning
Buttons example
In the following example, we will position two buttons in the bottom right corner of the window. We will use the pack manager.#!/usr/bin/wishWe will have two frames. There is the base frame and an additional frame, which will expand in both directions and push the two buttons to the bottom of the base frame. The buttons are placed in a horizontal box and placed to the right of this box.
# ZetCode Tcl/Tk tutorial
#
# In this script, we use pack manager
# to position two buttons in the
# bottom right corner of the window.
#
# author: Jan Bodnar
# last modified: March 2011
# website: www.zetcode.com
frame .fr
pack .fr -fill both -expand 1
frame .fr.pnl -relief raised -borderwidth 1
pack .fr.pnl -fill both -expand 1
ttk::button .fr.cb -text "Close"
pack .fr.cb -padx 5 -pady 5 -side right
ttk::button .fr.ok -text "OK"
pack .fr.ok -side right
wm title . "buttons"
wm geometry . 300x200+300+300
frame .fr.pnl -relief raised -borderwidth 1We create another
pack .fr.pnl -fill both -expand 1
frame widget. This widget takes the bulk of the area. We change the border of the frame so that the frame is visible. By default it is flat. The packmanager expands the frame in both directions. Horizontal and vertical. ttk::button .fr.cb -text "Close"A close button is created. It is put into a horizontal box. The -side option will create a horizontal box layout, in which the button is placed to the right of the box. The -padx and the -pady options will put some space between the widgets. The -padx puts some space between the button widgets and between the close button and the right border of the root window. The -pady puts some space between the button widgets and the borders of the frame and the root window.
pack .fr.cb -padx 5 -pady 5 -side right
pack .fr.ok -side rightThe ok button is placed next to the close button. With 5px space between them.
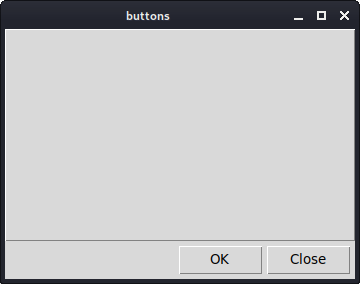
Figure: Buttons example
Calculator
We will use a Tk grid geometry manager to create a skeleton of a calculator.#!/usr/bin/wishIn this example, we use the grid manager is used to organize buttons in the frame container widget.
# ZetCode Tcl/Tk tutorial
#
# In this script, we use the grid manager
# to create a skeleton of a calculator.
#
# author: Jan Bodnar
# last modified: March 2011
# website: www.zetcode.com
frame .fr -padx 5 -pady 5
pack .fr -fill both -expand 1
ttk::style configure TButton -width 8 -height 8 -font "serif 10"
entry .fr.ent
grid .fr.ent -row 0 -columnspan 4 -sticky we
ttk::button .fr.cls -text "Cls"
grid .fr.cls -row 1 -column 0
ttk::button .fr.bck -text "Back"
grid .fr.bck -row 1 -column 1
ttk::button .fr.lbl
grid .fr.lbl -row 1 -column 2
ttk::button .fr.clo -text "Close"
grid .fr.clo -row 1 -column 3
ttk::button .fr.sev -text "7"
grid .fr.sev -row 2 -column 0
ttk::button .fr.eig -text "8"
grid .fr.eig -row 2 -column 1
ttk::button .fr.nin -text "9"
grid .fr.nin -row 2 -column 2
ttk::button .fr.div -text "/"
grid .fr.div -row 2 -column 3
ttk::button .fr.fou -text "4"
grid .fr.fou -row 3 -column 0
ttk::button .fr.fiv -text "5"
grid .fr.fiv -row 3 -column 1
ttk::button .fr.six -text "6"
grid .fr.six -row 3 -column 2
ttk::button .fr.mul -text "*"
grid .fr.mul -row 3 -column 3
ttk::button .fr.one -text "1"
grid .fr.one -row 4 -column 0
ttk::button .fr.two -text "2"
grid .fr.two -row 4 -column 1
ttk::button .fr.thr -text "3"
grid .fr.thr -row 4 -column 2
ttk::button .fr.mns -text "-"
grid .fr.mns -row 4 -column 3
ttk::button .fr.zer -text "0"
grid .fr.zer -row 5 -column 0
ttk::button .fr.dot -text "."
grid .fr.dot -row 5 -column 1
ttk::button .fr.equ -text "="
grid .fr.equ -row 5 -column 2
ttk::button .fr.pls -text "+"
grid .fr.pls -row 5 -column 3
grid columnconfigure .fr 0 -pad 3
grid columnconfigure .fr 1 -pad 3
grid columnconfigure .fr 2 -pad 3
grid columnconfigure .fr 3 -pad 3
grid rowconfigure .fr 0 -pad 3
grid rowconfigure .fr 1 -pad 3
grid rowconfigure .fr 2 -pad 3
grid rowconfigure .fr 3 -pad 3
grid rowconfigure .fr 4 -pad 3
wm title . "calculator"
wm geometry . +300+300
ttk::style configure TButton -width 8 -height 8 -font "serif 10"We configure the themed
button widget to have a specific font and to have some internal padding. entry .fr.entThe
grid .fr.ent -row 0 -columnspan 4 -sticky we
entry widget is where the digits are displayed. The widget is placed at the first row and it will span all four columns. Widgets may not occupy all the space allotted by cells in the grid. The -sticky option will expand the widget in a given direction. In our case, we ensure, that the entry widget is expanded from left to the right. ttk::button .fr.cls -text "Cls"The cls button is placed at the second row, first column. Note that the rows and columns start at zero. The ttk::button is a themed button.
grid columnconfigure .fr 0 -pad 3We use the
...
grid rowconfigure .fr 0 -pad 3
columnconfigure and the rowconfigurecommands to define some space in grid columns and rows. This way we achieve that the buttons are separated by some space. 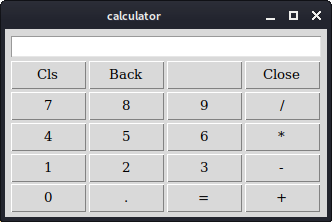
Figure: Calculator
Windows example
The following example creates the windows dialog using the grid geometry manager. The dialog comes from the JDeveloper application.#!/usr/bin/wishIn this example, we will use a
# ZetCode Tcl/Tk tutorial
#
# In this script, we use the grid
# manager to create a more complicated
# layout.
#
# author: Jan Bodnar
# last modified: March 2011
# website: www.zetcode.com
frame .fr -padx 5 -pady 5
pack .fr -fill both -expand 1
label .fr.lbl -text Windows
grid .fr.lbl -sticky w -pady 4 -padx 5
text .fr.area
grid .fr.area -row 1 -column 0 -columnspan 2 \
-rowspan 4 -padx 5 -sticky ewsn
ttk::button .fr.act -text Activate
grid .fr.act -row 1 -column 3
ttk::button .fr.cls -text Close
grid .fr.cls -row 2 -column 3 -pady 4
ttk::button .fr.hlp -text Help
grid .fr.hlp -row 5 -column 0 -padx 5
ttk::button .fr.ok -text OK
grid .fr.ok -row 5 -column 3
grid columnconfigure .fr 1 -weight 1
grid columnconfigure .fr 3 -pad 7
grid rowconfigure .fr 3 -weight 1
grid rowconfigure .fr 5 -pad 7
wm title . "Windows"
wm geometry . 350x300+300+300
label widget, a text widget and four buttons. label .fr.lbl -text WindowsThe label widget is created and put into the grid. If no column and row is specified, then the first column/row is assumed. The label sticks to west and it has some padding around its text.
grid .fr.lbl -sticky w -pady 4 -padx 5
text .fr.areaThe
grid .fr.area -row 1 -column 0 -columnspan 2 \
-rowspan 4 -padx 5 -sticky ewsn
text widget is created and starts from the second row, first column. It spans 2 columns and 4 rows. There is 4px space between the widget and the left border of the root window. Finally, it sticks to all the four sides. So when the window is resized, the text widget grows in all directions. grid columnconfigure .fr 1 -weight 1We define some spaces among widgets in the grid. The largest space is put between the
grid columnconfigure .fr 3 -pad 7
grid rowconfigure .fr 3 -weight 1
grid rowconfigure .fr 5 -pad 7
text widget and the buttons. 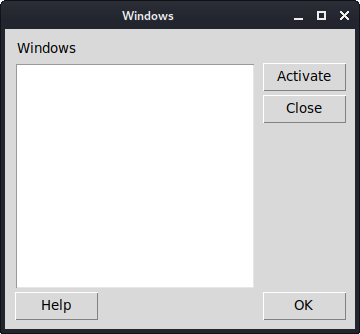
Figure: Windows example
In this part of the Tcl/Tk tutorial, we mentioned layout management of widgets.
No comments:
Post a Comment