Introduction to Jython Swing
In this part of the Jython Swing tutorial, we will introduce the Swing toolkit and create our first programs using the Jython programming language.The purpose of this tutorial is to get you started with the Swing toolkit with the Jython language. Images used in this tutorial can be downloaded here. I used some icons from the Tango icons pack of the Gnome project.
About
Swing library is an official Java GUI toolkit for the Java programming language. It is used to create Graphical user interfaces with Java. Swing is an advanced GUI toolkit. It has a rich set of components. From basic ones like buttons, labels, scrollbars to advanced components like trees and tables. Swing itself is written in Java. Swing is available for other languages too. For example Jython, JRuby, Groovy or Scala.Jython is an implementation of the Python programming language written in Java. Jython can import any Java class.
There are two basic ways to execute the examples in this tutorial. One way is to install a Python NetBeans plugin. It contains Jython as well. When you create a new Python project, be sure to select the Jython platform.
The other way is to download an installer from the jython.orgwebsite.
$ java -jar jython_installer-2.5.2rc2.jarWe install the Jython. You go through a series of dialogs.
$ java -jar jython.jar simple.pyWe have installed Jython in a selected directory. In this directory, we will find jython.jar file, which is used to execute Jython scripts.
$ cat /usr/local/bin/jythonOptionally, we can create a bash file which will automatically start our Jython scripts. We can then put the #!/usr/bin/local/jython path to our scripts.
#!/bin/bash
/home/vronskij/bin/jdk1.6.0_21/bin/java -jar /home/vronskij/bin/jython/jython.jar $1
Simple example
In our first example, we will show a basic window on the screen.#!/usr/local/bin/jythonWhile this code is very small, the application window can do quite a lot. It can be resized, maximized, minimized. All the complexity that comes with it has been hidden from the application programmer.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode Jython Swing tutorial
This example shows a simple
window on the screen.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: www.zetcode.com
last modified: November 2010
"""
from javax.swing import JFrame
class Example(JFrame):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setTitle("Simple")
self.setSize(250, 200)
self.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
self.setLocationRelativeTo(None)
self.setVisible(True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Example()
from javax.swing import JFrameWe import a
JFrame class. The JFrame is a top-level window with a title and a border. self.initUI()We delegate the creation of the user interface to the
initUI() method. self.setTitle("Simple")
We set the title of the window using the setTitle() method. self.setSize(250, 200)We set the size of the window.
self.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)This method ensures that the window terminates, if we click on the close button of the titlebar. By default nothing happens.
self.setLocationRelativeTo(None)We center the window on the screen.
self.setVisible(True)Finally, the window is showed on the screen.
Tooltip
A tooltip is a small rectangular window, which gives a brief information about an object. It is usually a GUI component. It is part of the help system of the application.#!/usr/local/bin/jythonIn the example, we set the tooltip for the frame and the button.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode Jython Swing tutorial
This code shows a tooltip on
a window and a button.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: www.zetcode.com
last modified: November 2010
"""
from javax.swing import JButton
from javax.swing import JFrame
from javax.swing import JPanel
class Example(JFrame):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
panel = JPanel()
self.getContentPane().add(panel)
panel.setLayout(None)
panel.setToolTipText("A Panel container")
button = JButton("Button")
button.setBounds(100, 60, 100, 30)
button.setToolTipText("A button component")
panel.add(button)
self.setTitle("Tooltips")
self.setSize(300, 200)
self.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
self.setLocationRelativeTo(None)
self.setVisible(True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Example()
panel = JPanel()We create a
self.getContentPane().add(panel)
JPanel component. It is a generic lightweight container. JFrame has an area, where you put the components called the content pane. We put the panel into this pane. panel.setLayout(None)By default, the
JPanel has a FlowLayout manager. The layout manager is used to place widgets onto the containers. If we call setLayout(None) we can position our components absolutely. For this, we use the setBounds() method. panel.setToolTipText("A Panel container")
To enable a tooltip, we call the setTooltipText() method. 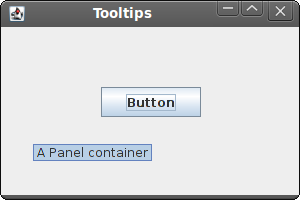
Figure: Tooltip
Quit button
In the last example of this section, we will create a quit button. When we press this button, the application terminates.#!/usr/local/bin/jythonWe position a
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
ZetCode Jython Swing tutorial
This program creates a quit
button. When we press the button,
the application terminates.
author: Jan Bodnar
website: www.zetcode.com
last modified: November 2010
"""
from java.lang import System
from javax.swing import JButton
from javax.swing import JFrame
from javax.swing import JPanel
class Example(JFrame):
def __init__(self):
super(Example, self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
panel = JPanel()
self.getContentPane().add(panel)
panel.setLayout(None)
qbutton = JButton("Quit", actionPerformed=self.onQuit)
qbutton.setBounds(50, 60, 80, 30)
panel.add(qbutton)
self.setTitle("Quit button")
self.setSize(300, 200)
self.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
self.setLocationRelativeTo(None)
self.setVisible(True)
def onQuit(self, e):
System.exit(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Example()
JButton on the window. We will add an action listener to this button. qbutton = JButton("Quit", actionPerformed=self.onQuit)
qbutton.setBounds(50, 60, 80, 30)
Here we create a button. We position it by calling the setBounds() method. The actionPerformed parameter specifies the method which is called, when we click on the button. def onQuit(self, e):The onQuit() method exits the application.
System.exit(0)
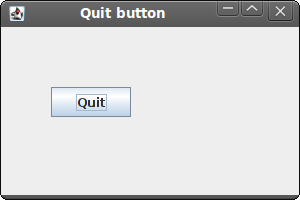
Figure: Quit button
This section was an introduction to the Swing toolkit with the Jython language.
No comments:
Post a Comment